Automatic urinalysis

An automated unit for chemical and microscopic examination of urine. This instruction video on automatic biochemical analysers was made in collaboration with the Dept. of Clinical Biochemistry and Haematology of the Faculty Hospital in Brno, the Dept. of Biochemistry, and the Data Processing Centre of the MU Fac. of Medicine in Brno. It is provided with a spoken commentary which, on the one hand, gives a static description of the individual components of the analyser and, on the other, accompanies individual demonstrations of its function. The video also contains a description and a demonstration of the functioning of the automated urine laboratory (automated unit for chemical and microscopic examination of urine iQ200).
Random access analyser (HITACHI 917)

The automatic biochemical analyser Hitachi 917 is a prototype of high-capacity selective analyser. It has a capacity of 800 photometric tests per hour and the possibility of selective choice out of a range of fifty biochemical tests. This involves spectrophotometric methods that utilise measurements of absorbance of the reaction mixture in a cuvette at various wavelengths. A part of the analyser is an ion-selective electrode module for the determination of sodium, potassium, and chlorides. The duration of the video is 17 min.
Essentials of Medical Chemistry and Biochemistry
The English text has been created for one-semester course of medical chemistry. It is assigned for the students of English program of General medicine and Dentistry studies. The textbook summarizes essential facts from chemistry and biochemistry. The selection of topics emphasizes the biochemical processes and the metabolic conversions of compounds occurring in the human body. The knowledge of presented facts is necessary for understanding metabolic processes on cellular and organ level in the following studies of biochemistry
Molecular biology
The terms "recombinant DNA technology", "DNA cloning", "molecular cloning", and "gene cloning" all refer to the same process: a transfer of a DNA fragment of interest from one organism to a self-replicating genetic element such as a bacterial plasmid. The DNA of interest can then be replicated (together with the rest of the plasmid) in a foreign host cell. This technology is a common practice in molecular biology labs today.
Protein preparation
This course contains five sub-courses, which consist of theoretical and practical parts. The individual sub-courses should provide students simple and quick approaches needed for solving basic scientific problems that could rise during the course of their bachelor, diploma or PhD study. The first set will allow students to gain knowledge about protein cloning, expression and purification. The second part focuses on biochemical characterization of enzymes via their enzymatic activity as well as protein-protein interactions. The third set will provide simple biochemical methods to detect protein-protein and protein-DNA interactions as well as monitor motor activity of protein.
Blood taking
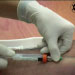
This video recording is destined for supplementation of the instruction in Clinical Biochemistry in biomedical disciplines and deals with the description of procedures used in the taking and processing of blood. It gives a concise documentation on the preparation of the patient prior to the taking and the procedure during the taking of venous blood. Emphasis is laid on the use of the closed system of blood taking. Mention is made of the transport and storage of samples, procedures of the taking of plasma and serum, and of obtaining and processing capillary blood.