Neural development and embryonic stem cell-based developmental modelling
This educational article titled “Neural development and embryonic stem cell-based developmental modelling“ describes how to investigate the roles of genes in human neural development using stem cell technologies and molecular biology techniques. This educational article is primarily focused on experimental practices. Thus this article is intended for postgraduate students (e.g. Master student, Diploma, and PhD students). However, the article is also suitable for undergraduate students, who are interested in stem cell biology and molecular biology. In the text, students will learn how to perform basic molecular biology techniques (e.g. gene cloning, making fusion protein, PCR and sequencing), and how to grow and to manipulate human embryonic stem cells (hESCs). Moreover, students will learn how to drive hESCs toward to neural fates.
Basic principles and molecular mechanisms regulating early development of mammals - physiology and pathology

This educational text titled “Basic principles and molecular mechanisms regulating early development of mammals - ¬physiology and pathology“ describes how embryogenesis proceeds in mammals. In this text, students will learn how the egg is fertilised, how the fertilised egg survives in the mother’s womb (called implatation), how the fertilised egg divides, how the blastocyst develops, how the implanted blastocyst undergos gastrulation or the three germ layers form, and how the brain, heart, muscle, and internal organs develop. Moreover, if the processes go awry, what the baby will be affected. This educational material is recommened to General Medical, Dental Medical students and the students who are taking a developmental biological course.
Molecular biology
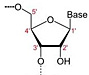
The terms "recombinant DNA technology", "DNA cloning", "molecular cloning", and "gene cloning" all refer to the same process: a transfer of a DNA fragment of interest from one organism to a self-replicating genetic element such as a bacterial plasmid. The DNA of interest can then be replicated (together with the rest of the plasmid) in a foreign host cell. This technology is a common practice in molecular biology labs today.
Protein preparation
This course contains five sub-courses, which consist of theoretical and practical parts. The individual sub-courses should provide students simple and quick approaches needed for solving basic scientific problems that could rise during the course of their bachelor, diploma or PhD study. The first set will allow students to gain knowledge about protein cloning, expression and purification. The second part focuses on biochemical characterization of enzymes via their enzymatic activity as well as protein-protein interactions. The third set will provide simple biochemical methods to detect protein-protein and protein-DNA interactions as well as monitor motor activity of protein.